Understanding Oxidative Stress: Causes, Consequences and Natural Solutions
Oxidative stress is a complex biomolecular phenomenon resulting from an imbalance between the production of free radicals and the body's intrinsic ability to neutralize them through antioxidants . Given its involvement in the cellular aging process and its potential impact on overall well-being, it is essential to thoroughly understand its mechanisms, causes, and the levers for action to maintain a formidable balance against the excessive formation of these reactive species.
The molecular mechanisms of oxidative stress
At the heart of our cells, mitochondria generate energy in the form of ATP through an electron transport chain. During this process, a small fraction of oxygen is partially reduced, giving rise to superoxide radicals ( O₂⁻ ) and then to hydrogen peroxides ( H₂O₂ ).
Under normal conditions, specialized enzymes such as superoxide dismutase (SOD), catalase, and glutathione peroxidase work to convert these species into harmless water or oxygen. When this enzymatic protection is overwhelmed, free radicals can attack membrane lipids, proteins, and even DNA, initiating a cascade of oxidations that weakens cell structure and function.
Lipid peroxidation causes the formation of malondialdehyde and other aldehydes that disrupt membrane permeability.
At the protein level , oxidation leads to the formation of abnormal disulfide bridges or carbonylation, radically altering conformation and enzymatic activity.
DNA oxidation can generate lesions such as 8-oxo-2′-deoxyguanosine, an early marker of genomic damage.
Internal and external factors responsible for the imbalance
Oxidative balance is influenced by two main categories of factors. On the one hand, endogenous parameters include energy metabolism, hormonal status, and the ability to recycle glutathione in its reduced form (GSH). On the other hand, exogenous factors play a crucial role:
Air pollution , particularly PM2.5 and PM10 particles, induces the production of hydroxyl radicals and nitrogen oxides; these reactive molecules penetrate the pulmonary alveoli and diffuse into the bloodstream, triggering systemic inflammation and a chronic oxidative cascade. Ultraviolet rays (UV-A and UV-B), meanwhile, generate oxygen singlet species in the epidermis, accelerating the peroxidation of skin lipids.
Tobacco and alcohol are major sources of oxidative stress. The thousands of toxic compounds present in cigarette smoke, as well as ethanol and its metabolites, directly stimulate the generation of free radicals and inhibit the expression of genes coding for antioxidant enzymes.
Lifestyle , whether overly sedentary or based on extreme exercise without adequate recovery, alters mitochondrial production of reactive species. Furthermore, insufficient nutritional intake of essential micronutrients (vitamins C and E, selenium, zinc) weakens glutathione regeneration and the ability to convert peroxides into harmless molecules.
Chronic psychological stress , via the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal pathway, raises cortisol levels and promotes oxidative stress by increasing oxygen consumption and the production of free radicals in muscle and brain tissues.

Consequences for health and aging
When oxidative stress persists, it actively contributes to cellular and tissue aging. In the case of the skin, the combination of lipid peroxidation and decreased collagen synthesis leads to a loss of firmness, the premature appearance of wrinkles , and a dullness of the complexion. Damage to keratinocytes and fibroblasts also disrupts wound healing and the skin barrier.
At the vascular level, the attack on endothelial cells by free radicals reduces the bioavailability of nitric oxide (NO), a key factor in vasodilation. This decrease in endothelial function can promote local inflammation and stiffening of arterial walls, contributing to perfusion disorders and reduced vascular plasticity.
In the brain, redox balance is crucial for maintaining neurotransmission and synaptic plasticity. Excessive oxidative stress can alter tau proteins and beta-amyloid, factors involved in cognitive decline and memory disorders.
Dietary approaches to boost your antioxidant potential
Diet is the primary lever for modulating oxidative balance. Polyphenols, abundant in berries such as blueberries and raspberries, act as free radical scavengers and modulators of antioxidant signaling pathways (Nrf2). Glucosinolates from cruciferous vegetables, particularly sulforaphane from broccoli, induce the expression of phase II detoxification enzymes.
Regular consumption of leafy green vegetables (spinach, kale) provides not only vitamin C but also carotenoids (lutein, beta-carotene) that interact with lipid membranes to stabilize them. Walnuts and chia seeds provide omega-3 fatty acids, precursors of resolvins and protectins, lipids specialized in reducing inflammation.
Lifestyle and recovery strategies
Engaging in moderate physical activity, combined with quality sleep, is essential for activating oxidative repair pathways. During deep, slow-wave sleep, neurons preferentially produce antioxidant enzymes, contributing to the restoration of depleted glutathione. Relaxation techniques (meditation, heart coherence) decrease cortisol release and thus reduce the production of free radicals secondary to emotional stress.
During recovery phases, modulating peri-exercise nutrition, particularly controlled intake of protein and low glycemic index carbohydrates, prevents mitochondrial hyperactivity and limits superoxide production.
External protection: skin and mucous membranes
The skin barrier can be supported by the application of broad-spectrum UV filters and cosmetics rich in topical antioxidants (stabilized vitamin C, coenzyme Q10, niacinamide). In urban environments, the use of serums based on green tea extracts or vitamin E forms a protective film against particulate pollution.

Role of dietary supplements
When dietary and behavioral measures reach their limits, high-purity supplements can provide targeted support. Formulations based on liposomal vitamin C, reduced glutathione, and green tea polyphenols deliver active molecules in controlled concentrations, without claiming to cure any specific condition.
These Absolute Relaxation gummies combine a patented saffron extract, a star among adaptogenic plants , and vitamin B6 to reduce stress and promote relaxation naturally. These saffron gummies are sugar-free, vegan, and made in France.
Optimize sleep for maximum antioxidant effect
A complete sleep cycle is essential for nighttime antioxidant regeneration. Sleep gummies combine melatonin, vitamins B5 and B6, linden, and passionflower to promote sleep onset without disrupting sleep structure.

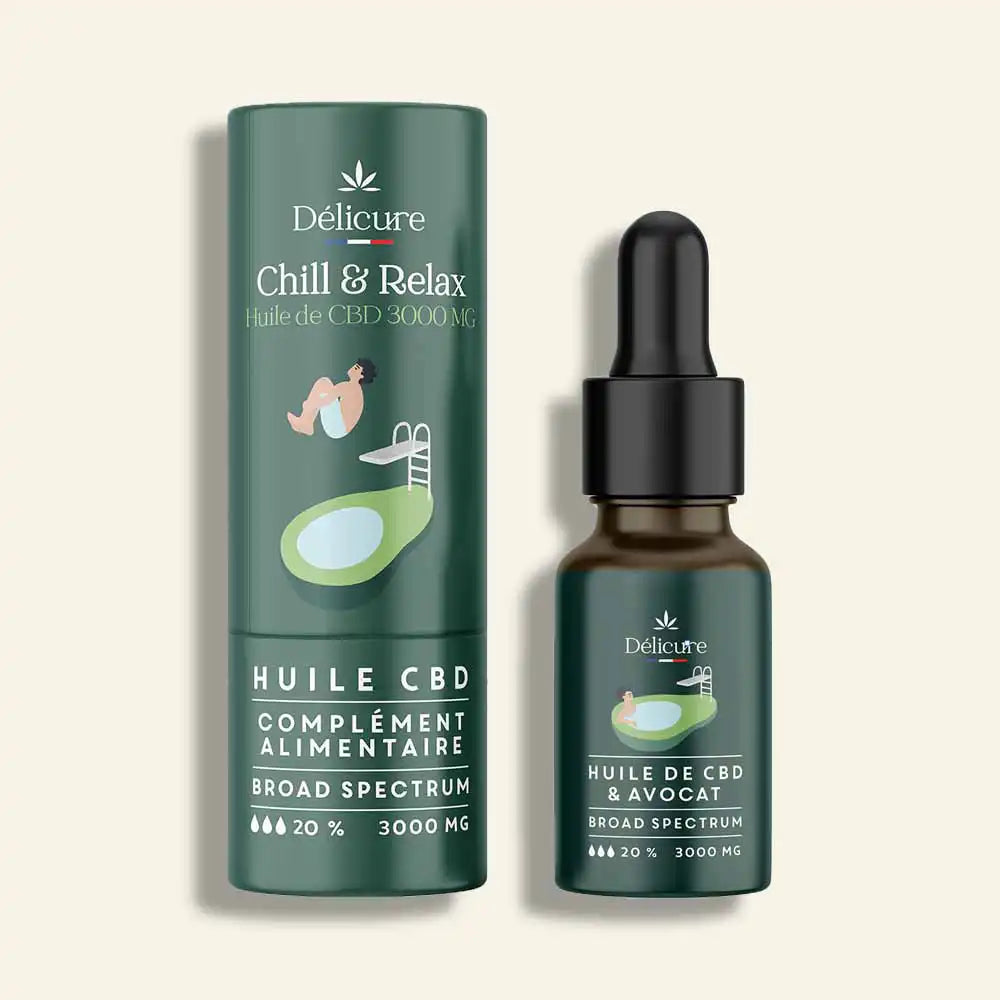
Focus on CBD extracts and other active ingredients
Cannabidiol-based candies and natural CBD oils made from avocado and sweet almond are commonly consumed for relaxation; these products are manufactured in compliance with French food supplement standards.
In conclusion: Oxidative stress remains a constant challenge for the body, but implementing an integrated strategy — combining a diet rich in antioxidants, a rigorous lifestyle, skin protection and the use of quality supplements — makes it possible to significantly reduce redox imbalance and protect your cells from oxidative damage.