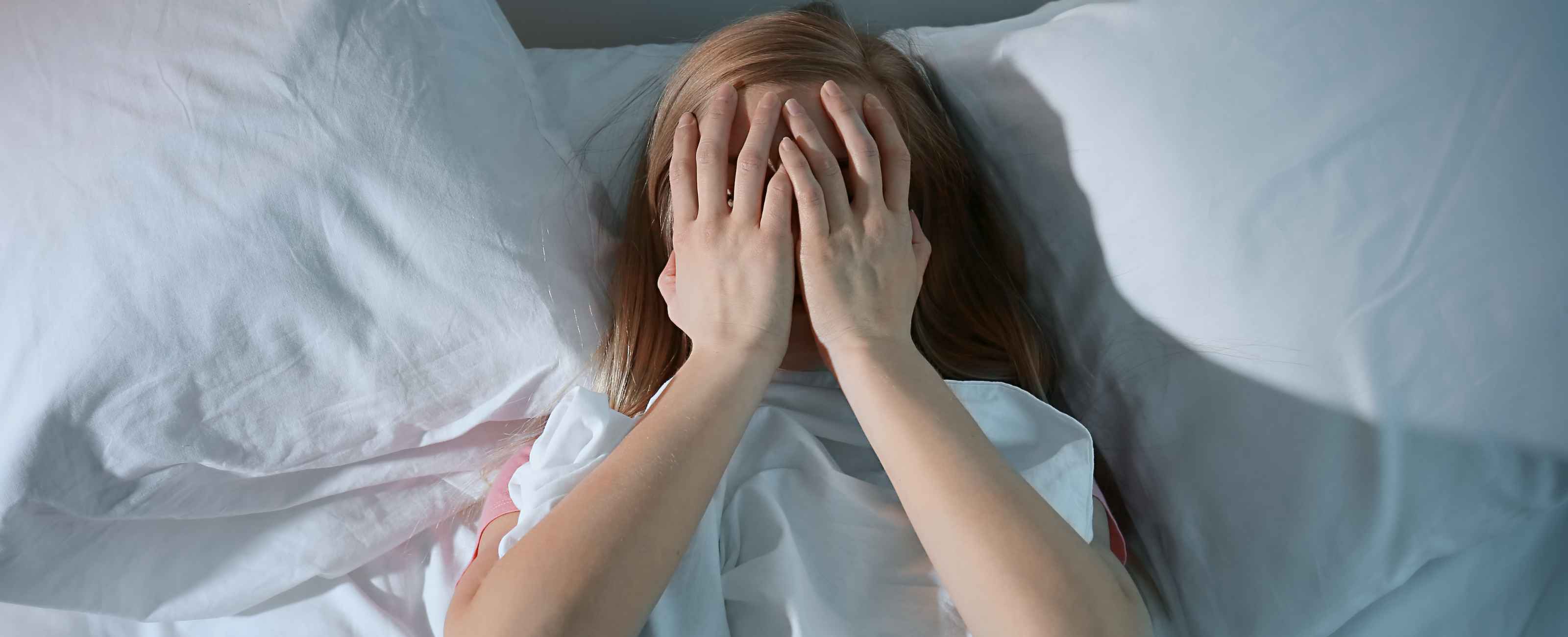
What is dopamine?
Dopamine is a neurotransmitter released naturally in the human body. It is synthesized by certain nerve cells from an amino acid called tyrosine (a constituent of food proteins).
The so-called “dopaminergic” cell bodies are located in the midbrain (middle part of the brain). They spread to the frontal cortex, amygdala and striatum.
Dopamine is also called a molecule, which has the role of communicating information between neurons.

How is dopamine secreted?
This molecule is secreted by a few neurons located in the synapses (areas located between neurons).
These neurons are few in number in the brain, they will cause a release of dopamine in the nucleus accumbens, as well as stimulation of the reward system which manages desire, pleasure and emotions. This system also plays an essential role in the establishment of dependence or addiction phenomena.
The molecule will bind to receptors located on other neurons, thus allowing the transmission of information from one neuron to another.
However, there are several types of receptors. The effect of dopamine will therefore vary depending on the neuron which releases it, and the receptor which receives it or, on the contrary, does not receive it.
Dopamine is released by the brain during experiences that it links to pleasure. As a result, it is called the “happiness hormone” or “desire molecule”.

What is the difference between dopamine and serotonin?
Like dopamine, serotonin is a hormone that contributes to feelings of fulfillment and satisfaction. It is created naturally by the brain from tryptophan, an amino acid.
This hormone helps regulate behavior, mood , anxiety and even learning, then boost motivation and decision-making.
The use of serotonin is dedicated to the treatment of depression, in particular thanks to serotonergic antidepressants.
Dopamine, for its part, represents an immediate pleasure hormone. It appears following a gesture that triggers contentment, such as the announcement of good news, or the taste of a sweet substance or a cigarette.
A balance between serotonin and dopamine is beneficial to the body. This regulates mood and develops initiative.

What are the effects of dopamine?
Dopamine is a neurotransmitter involved in certain behavioral and personality traits.
Indeed, dopamine plays a role in improving attention and motivation, encouraging exploration, promoting the functioning of the kidneys and heart, as well as developing addictions, love and sexual pleasure.
Drugs, like cocaine, have the particularity of increasing dopamine activity, which therefore creates addiction.

What are the effects of a lack or overdose of dopamine on health?
A lack of dopamine has effects on health, they are associated with a lack of motivation, fatigue, memory loss or even addictive behaviors (drugs, alcohol, tobacco, etc.).
People with Parkinson's disease are most likely to be deficient in dopamine. Indeed, this disease can disrupt the secretion of this molecule .
Parkinson's disease causes the destruction of certain receptors in neurons responsible for controlling body movements. This triggers the tremors, freezes and motor slowness that characterize Parkinson's disease. There are medications to counter these symptoms and promote the synthesis and activity of dopamine.
Otherwise, in the event of an excess of dopamine, certain areas of the brain increase aggression and cause symptoms linked to schizophrenia to develop. Patients who suffer from it are treated with certain medications which have the effect of preventing dopamine from attaching to these receptors.
How is dopamine level measured?
To measure the level of this hormone, it is necessary to measure in the blood, urine or cerebrospinal fluid the quantity of a substance called HVA (homovanillic acid) and another substance called DOPAC. They are dopamine breakdown products.