What can stress cause?
Stress is a natural and physiological reaction of the body which allows us to flee or cope depending on the situation we find ourselves in.
If stress is controlled, lasts for a short period of time and does not cause unpleasant physical sensations, it is considered a driving force and performance accelerator. A good bout of stress allows you to run away from an aggressor, to revise more effectively before an important exam, or to give a public speech even better than in rehearsals.
However, if stress is chronic and too intense, it can decrease performance and have serious effects on mental and physical health.
When exposed to stress, the body generates an adaptation reaction consisting of three stages: the alarm phase, the resistance phase and the exhaustion phase.
The different phases of stress

As with sleep, stress is broken down into these three distinct phases:
- The alarm phase: the body prepares for fight or flight, the first symptoms of stress begin to be felt. To defend itself, the body produces cortisol (a stress hormone) and adrenaline to increase its energy level, heart rate, blood pressure and body temperature. Alertness, thinking and senses (sight, smell, hearing, etc.) are thus greatly increased during this phase.
- The resistance phase: if stress persists, the body enters the resistance phase. The body tries to find a new balance by secreting more cortisol, and by producing neurotransmitters in large quantities such as dopamine (linked to motivation) and serotonin (linked to well-being).
- The exhaustion phase: If stress is prolonged or intensified, the body exhausts its resources (physical, emotional and mental) and enters the exhaustion phase. The main signs of this phase are chronic fatigue, irritability, high anxiety, or a weakening of the immune system.
The different symptoms of stress

Each individual reacts differently to stress, which means that reactions are very varied. Some people somatize and experience physical symptoms, while others suffer from mood swings or loss of self-confidence.
Stress-related symptoms can be physical, psychological or emotional. The most common are fatigue, irritability, trembling, crying, cognitive difficulties (concentration, attention, learning, etc.), various pains (stomach, head, etc.), skin manifestations (eczema, hives), hair loss, heart palpitations, eating disorders, sleep disorders or even a depressive or nervous state.
Stress-related symptoms can occur in many situations (at work, at school, during pregnancy, etc.) and can have different causes such as traffic pressure, bad news, work overload, an important exam, relationship difficulties, financial problems or even a health problem.
The effects of stress on the body

The effects of stress on the body can be more significant than we imagine, especially since we often feel stress without being fully aware of it. However, our body sends us various warning signals that it is essential to recognize and interpret in time. Discover below the main impacts of stress on health and why it is crucial to take them into consideration.
1. A weakened immune system
When we are subjected to prolonged stress , the body secretes certain hormones in excess (notably cortisol). In the long term, this excessive production disrupts the normal functioning of the immune system.
- Consequence : The natural defenses are weakened, making the body more vulnerable to infections and common illnesses (colds, flu, etc.).
- Why you should pay attention : A weak immune system can lead to chronic fatigue, slow healing of injuries, and increase the likelihood of developing more serious illnesses.
2. Muscle and joint pain
Stress often leads to increased muscle tension , which particularly affects the back, neck, shoulders and legs.
- Consequence : Diffuse pain appears, sometimes difficult to relieve, because its origin is not purely organic but linked to a state of prolonged tension.
- Why pay attention to it : In the long term, this pain can lead to poor posture, aggravate certain pathologies (lower back pain, neck pain, etc.) and significantly reduce quality of life.
3. Headaches and neurological disorders
In addition to muscle pain, stress can manifest itself through recurring headaches : tension headaches or migraines, in particular.
- Associated symptoms : Mood swings, difficulty concentrating or even temporary memory loss are sometimes observed.
- Why you should be aware : Chronic pain and cognitive impairment (irritability, memory lapses) can negatively impact professional and personal life, creating a vicious cycle of additional stress.
4. Digestive disorders
The digestive system is particularly sensitive to hormonal and nervous variations caused by stress.
- Common effects : Stomach ache, gastroesophageal reflux, nausea or diarrhea.
- Irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) : Stress can aggravate or trigger this syndrome, characterized by bloating, diffuse abdominal pain and digestive disorders (constipation and/or diarrhea).
- Why you should be aware : Long-term digestive issues can lead to poor absorption of nutrients and disrupt the body's overall balance.
5. Cardiovascular risks
Chronic stress puts significant strain on the cardiovascular system , increasing heart rate and blood pressure.
- Consequences : High blood pressure, coronary heart disease and increased risk of myocardial infarction or stroke.
- Aggravating factors : People who already have coronary heart disease are even more exposed, as are those with risk factors (smoking, being overweight, being sedentary, etc.).
- Why you should be aware : Heart problems can come on suddenly and have serious long-term health consequences.
Stress affects different systems in our body: immune, muscular, neurological, digestive and cardiovascular. It is therefore essential to quickly identify warning signs (fatigue, pain, mood or transit disorders) in order to implement stress management strategies and best preserve one's health.
Tips to reduce stress
Fortunately, there are effective solutions to reduce stress and prevent its adverse effects.
Here are 5 simple tips to apply in everyday life:
- Exercise: Exercise is a real stress reliever, it allows the brain to release a series of calming hormones and neurotransmitters that help to better manage stress (endorphins, dopamine or serotonin). Practicing at least 30 minutes of daily physical activity thus offers a feeling of well-being and promotes a state of relaxation.
- Meditate: Meditation is an activity that helps to relieve stress and pain, better manage emotions, improve mood and promote relaxation. Through breathing, meditation helps to free the mind from ideas of the past and worries about the future, to focus only on the present moment.
- Develop your creativity: doing an artistic activity (music, writing, drawing, painting, dancing, etc.) is effective for relaxing and reducing stress. There are adult coloring books that are useful for promoting concentration, freeing and calming the mind.
- Laugh and socialize: Laughing is an action that can provoke positive emotions during a stressful situation, and thus help to overcome stress more easily. In addition, spending time and exchanging with certain people on different aspects of life can reassure, comfort and improve mood.
- Use anti-stress plants: many plants have anti-stress properties that are effective in combating anxiety, nervousness and anguish. They can be consumed in the form of infusions, tablets, capsules or even gummies.
Délicure offers stress gummies . Vegan, sugar-free, natural and made in France to reduce the harmful effects of stress on the body. They contain a patented saffron extract, 10 times more concentrated in active ingredients than other extracts on the market as well as vitamin B6 (essential for the synthesis of certain neurotransmitters).
A course of these gummies has the effect of protecting the nervous system against stress and anxiety, and thus promotes relaxation and well-being.
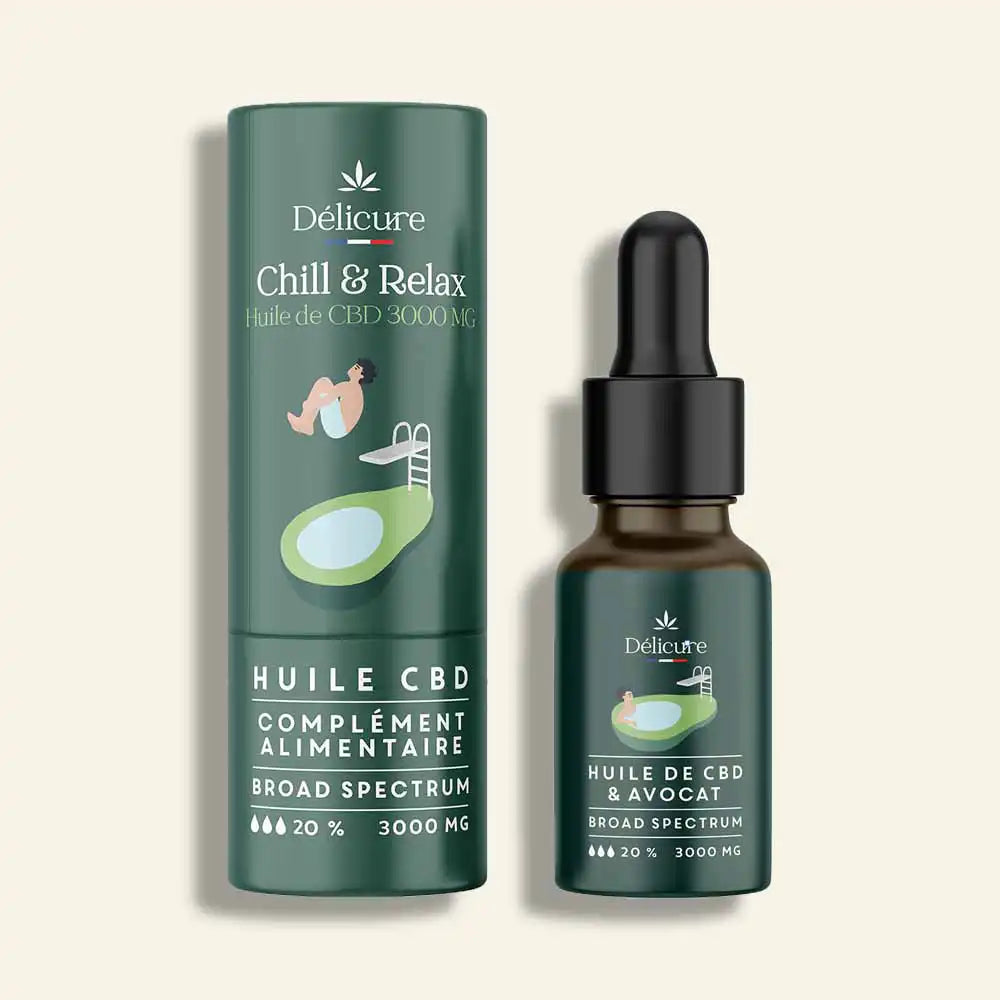
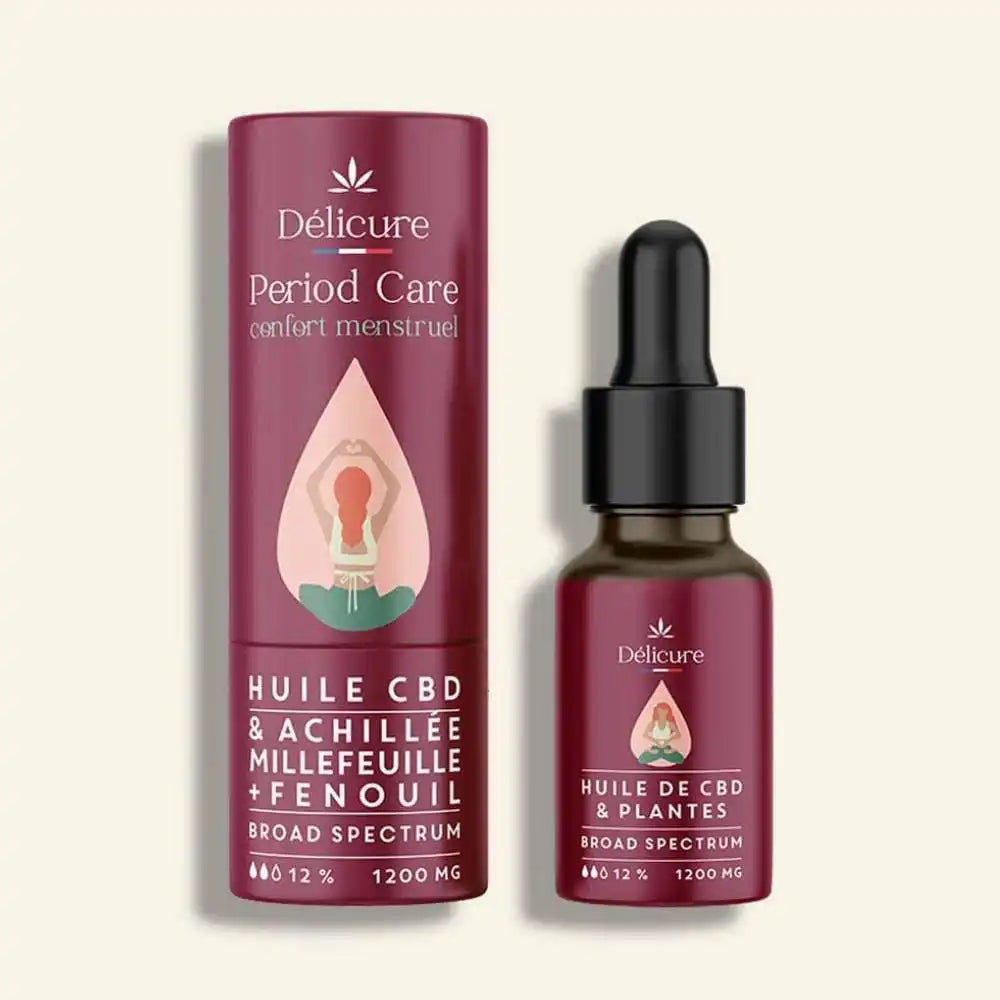
Délicure also offers CBD products in the form of CBD oils , gummies and CBD candies . Designed for stress, sleep and muscle comfort, they are made in France with high quality CBD, and do not contain THC.
Increasingly popular in France, CBD is a molecule derived from the hemp plant, known for its relaxing and pain-relieving effects. Unlike THC, it does not cause psychoactive effects and does not create addiction. Consuming CBD can therefore help combat stress and relieve the pain caused by it.
They can be consumed at any time of the day, during a stressful situation or a state of overwork. Being natural, they do not cause side effects, nor addiction, and have no danger to health.
It is obviously recommended to consult a doctor if you suffer from chronic stress or severe anxiety disorders that affect your quality of life, to find appropriate medical treatment.